Updated Result
05/03/28 (Mw 8.5) , Sumatra Earthquake
Ozgun Konca, Caltech
DATA Process and Inversion
This is an update of our preliminary result, and these results are published in Konca et al., 2007 (see reference list below) . This source model is obtained by joint inversion of 16 continuous GPS stations, about 90 coral uplift and subsidence measurements (Briggs et al., 2006) and teleseismic P and S waveforms. We use the epicenter of the USGS (Lon.=97.01 deg.; Lat.=2.01 deg.) with a hypocenter depth of 30 km. The dip and moment of the earthquake was carefully determined by simutaneously fitting normal mode excitation amplitudes and near-field geodetic data. The resulting best fit dip angle is 10° with moment of 1x10**29 dyne-cm. See Konca et al., 2007 for the detailed study of Nias Earthquake.Cross-section of slip distribution
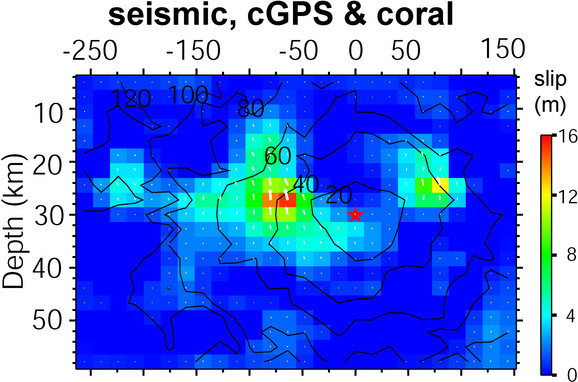
Figure: The big black arrow shows the fault's strike. The colors show the slip amplitude and white arrows indicate the direction of motion of the hanging wall relative to the footwall. Contours show the rupture initiation time and the red star indicates the hypocenter location.
Comparison of data and synthetic seismograms
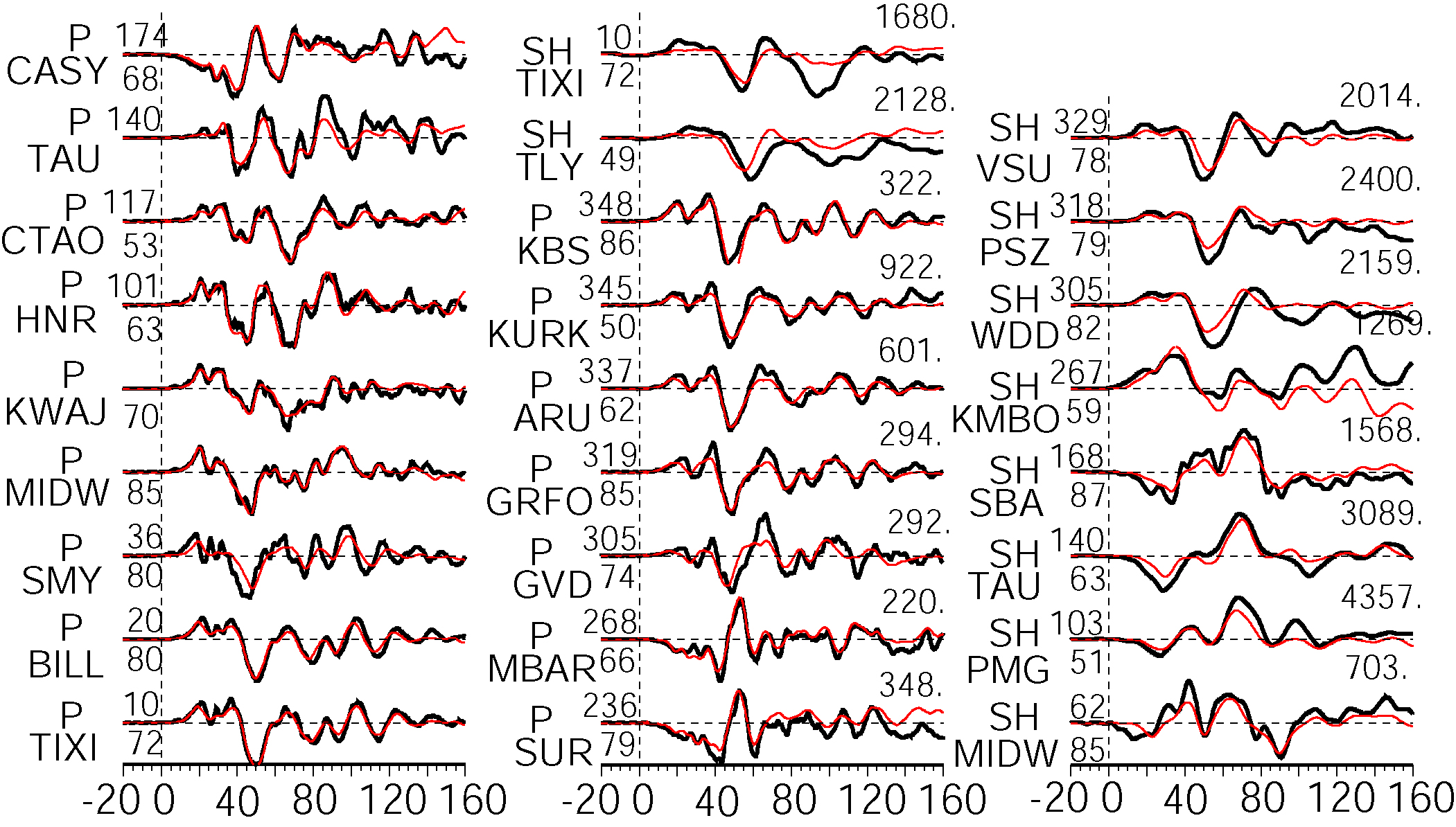
Figure: The Data are shown in black and the synthetic seismograms are plotted in red. Both data and synthetic seismograms are aligned on the P or SH arrivals. The number at the end of each trace is the peak amplitude of the observation in micro-meter. The number above the beginning of each trace is the source azimuth and below it is the epicentral distance.
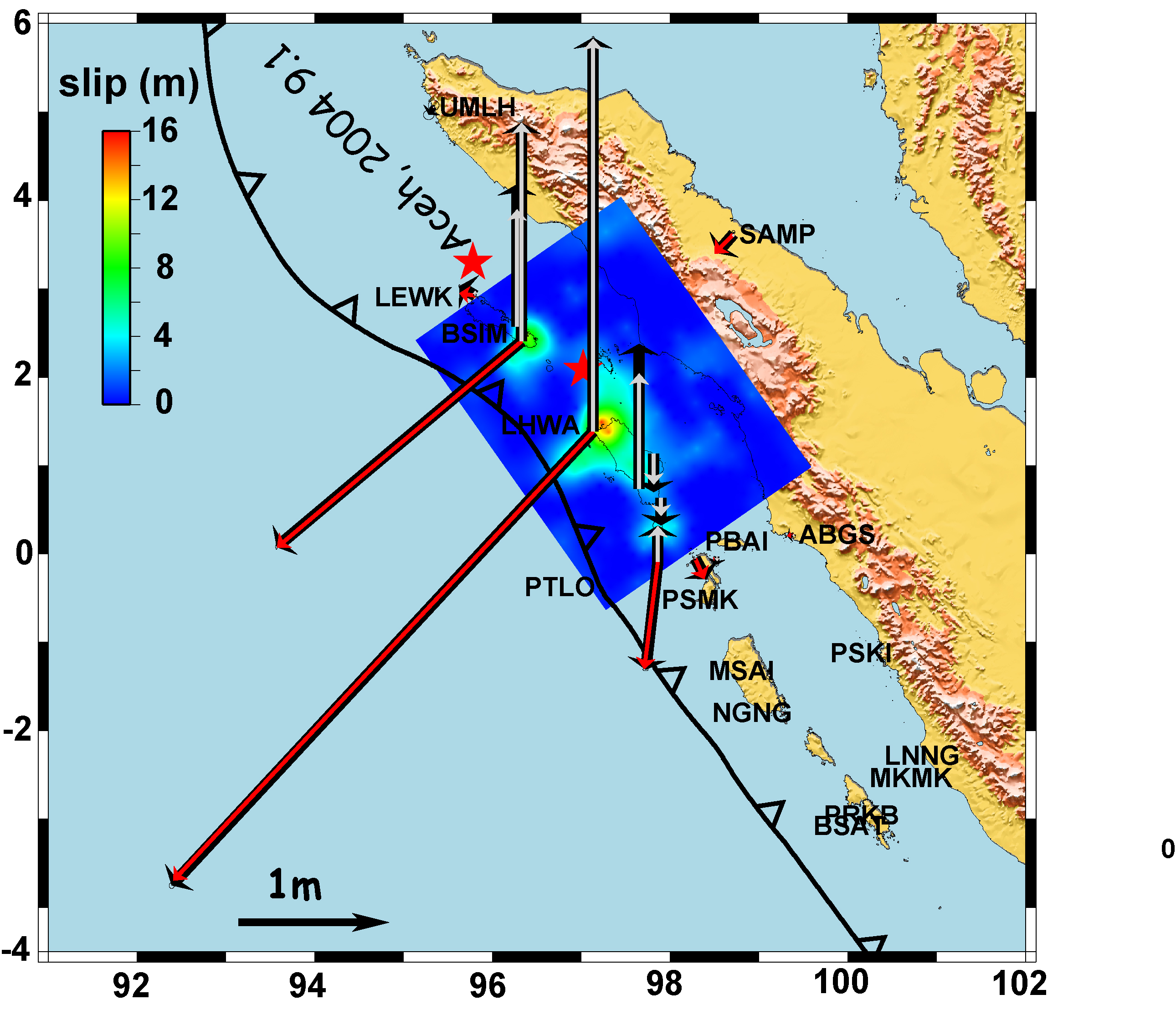
Figure: Surface projection of the slip distribution and GPS fits. GPS data vectors are shown in black, the fits tothe horizontal component is in red and verticals in gray
Download
(Slip Distribution)| SUBFAULT FORMAT | CMTSOLUTION FORMAT | SOURCE TIME FUNCTION |
References
Ji, C., D.J. Wald, and D.V. Helmberger, Source description of the 1999 Hector Mine, California earthquake; Part I: Wavelet domain inversion theory and resolution analysis,Bassin, C., Laske, G. and Masters, G., The Current Limits of Resolution for Surface Wave Tomography in North America, EOS Trans AGU, 81, F897, 2000.
Konca,A. Ozgun, Vala Hjorleifsdottir, Teh-Ru Alex Song, Jean-Philippe Avouac, Don V. Helmberger, Chen Ji, Kerry Sieh, Richard Briggs, Aron Meltzner, Rupture kinematics of the 2005, Mw 8.6, Nias- Simeulue earthquake from the joint inversion of seismic and geodetic data,
Briggs R.W., K. E. Sieh, A.J. Meltzner, D. H. Natawidjaja, J. Galetzka, B.W. Suwargadi, Y. Hsu, M. Simons, N. D. Hananto, D. Prayudi and I. Suprihanto (2006). "Deformation and slip along the Sunda megathrust in the great 2005 Nias-Simeulue earthquake.? Science 311(5769): 1897-1901
GCMT project: http://www.globalcmt.org/
USGS National Earthquake Information Center: http://neic.usgs.gov
Global Seismographic Network (GSN) is a cooperative scientific facility operated jointly by the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS), the United States Geological Survey (USGS), and the National Science Foundation (NSF).
‹Back to Slip Maps for Recent Large Earthquakes home page
© 2004 Tectonics Observatory :: California
Institute of Technology :: all rights reserved